Data Mining
The amount of data stored on computer is constantly increasing, coming from:
- IoT data
- Social data
- Data on purchases
- Banking and credit card transaction
The first step is to collect data in a data set. This step can be automated through artificial intelligence increasing the analytical power.
From on side, data is more and more and on the other side, hardware becomes more powerful and cheaper each day.
At the same time, managers are more and more willing to rely on data analysis for their business decisions. The information resource is a precious asset to overcoming competitors.
Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning and Data Mining
Although strongly interrelates, the term machine learning is formally distinct from the term Data Mining which indicates the computational process of pattern discovery in large datasets using machine learning methods, artificial intelligence, statistics and databases.
Data Mining - definition
Complex extraction of implicit, previously unknown and potentially useful data from the information. Exploration and analysis, using automated and semi-automatic systems, of large amounts of data in order to find significant patterns through statistics.
We do not just need to find results, but we need results to be USEFUL.
Analytics
Analytics refers to software used to discover, understand and share relevant pattern in data. Analytics are based on the concurrent use of statistics, machine learning and operational research techniques, often exploiting visualization techniques.
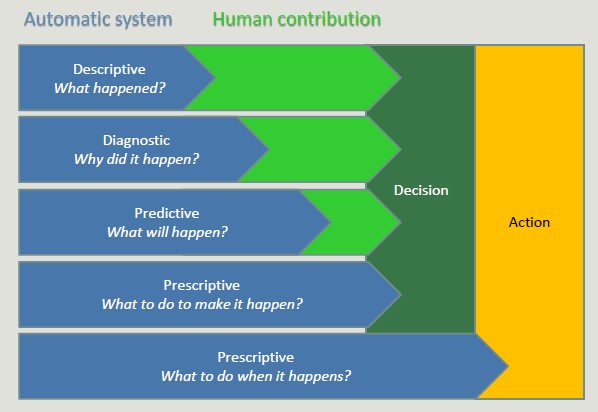
Prescriptive systems generate much value but it is extremely complex. Companies should start simple, adopting simple descriptive analytics solutions, and then move on. It is risky to skip intermediate steps.
BI adoption path
When we decide to digitalize a company, the adoption of BI solutions is incremental and rarely allows steps to be skipped. This is because it is risky, costly and useless to adopts advanced solutions before completely exploiting simple ones.
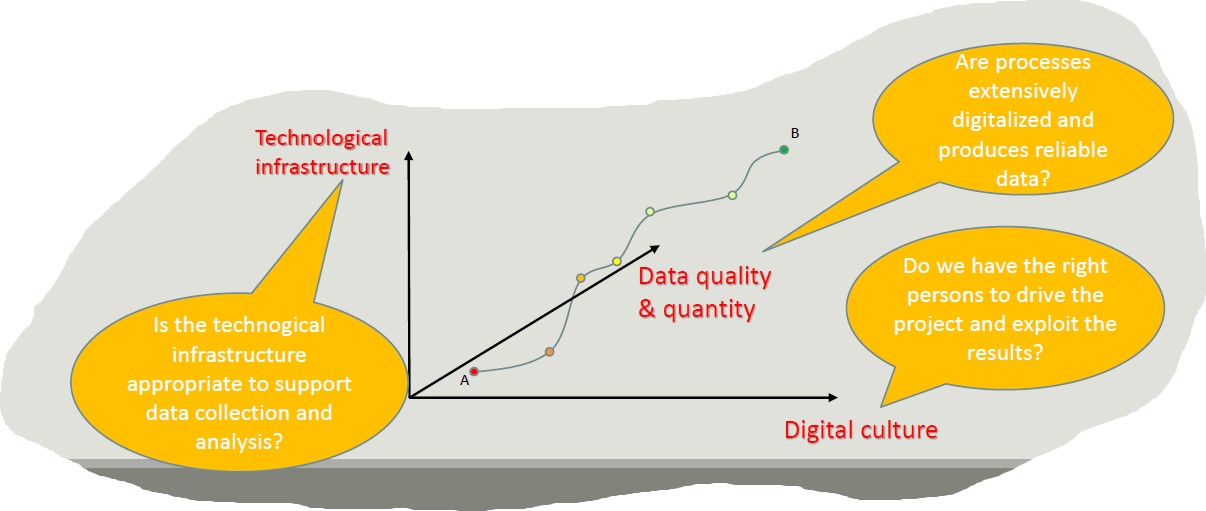
The goal is to create a data-driven company, where managers are supported by data.
- Decisions are based on quantitative rather than qualitative knowledge.
- Process and knowledge are an asset of the company and are not lost if managers change
The gap between a data-driven decision and a good decision is a good manager
Adopting a data-driven mindset goes far beyond adopting a business intelligence solution and entails:
- Create a data culture
- Change the mindset of managers
- Change processes
- Improve the quality of all the data
Digitalization is a journey that involves three main dimensions:
Pattern
A pattern is a synthetic representation rich in semantics of a set of data. It usually expresses a recurring pattern in data, but can also express an exceptional pattern.
A pattern must be:
- Valid on data with a certain degree of confidence
- It can be understood from the syntax and semantic point of view, so that the user can interpret it
- Previously unknown and potentially useful, so that users can take actions accordingly
When we distinguish between a manual technique (DW) and an automatic technique is the creation of a small subset of data which is rich in semantics.
The process begins with a huge multi-dimension cube of data, then grouping and selection techniques are adopted, creating a pattern.
Pattern types:
- Association rules (logical implications of the dataset)
- Classifiers (classify data according to a set of priori assigned classes)
- Decision trees (identify the causes that lead to an event, in order of importance)
- Clustering (group elements depending on their characteristics)
- Time series (detection of recurring or atypical patterns in complex data sequences)
Data Mining Applications
Predictive Systems
Exploit some features to predict the unknown values of other features (classification and regression).
Descriptive Systems
Find user-readable patterns that can be understood by human users (clustering, association rules, sequential pattern).
Classification - Definition
Given a record set, where each record is composed by a set of attributes (one of them represents the class of the record), find a model for the class attribute expressing the attribute value as a function of the remaining attributes.
Given a feature (defined at priori), define weather a user belongs to that feature
This model must work even when the record is not given. Unclassified record must be assigned to a class in the most accurate way.
A test set is used to determine the model accuracy.
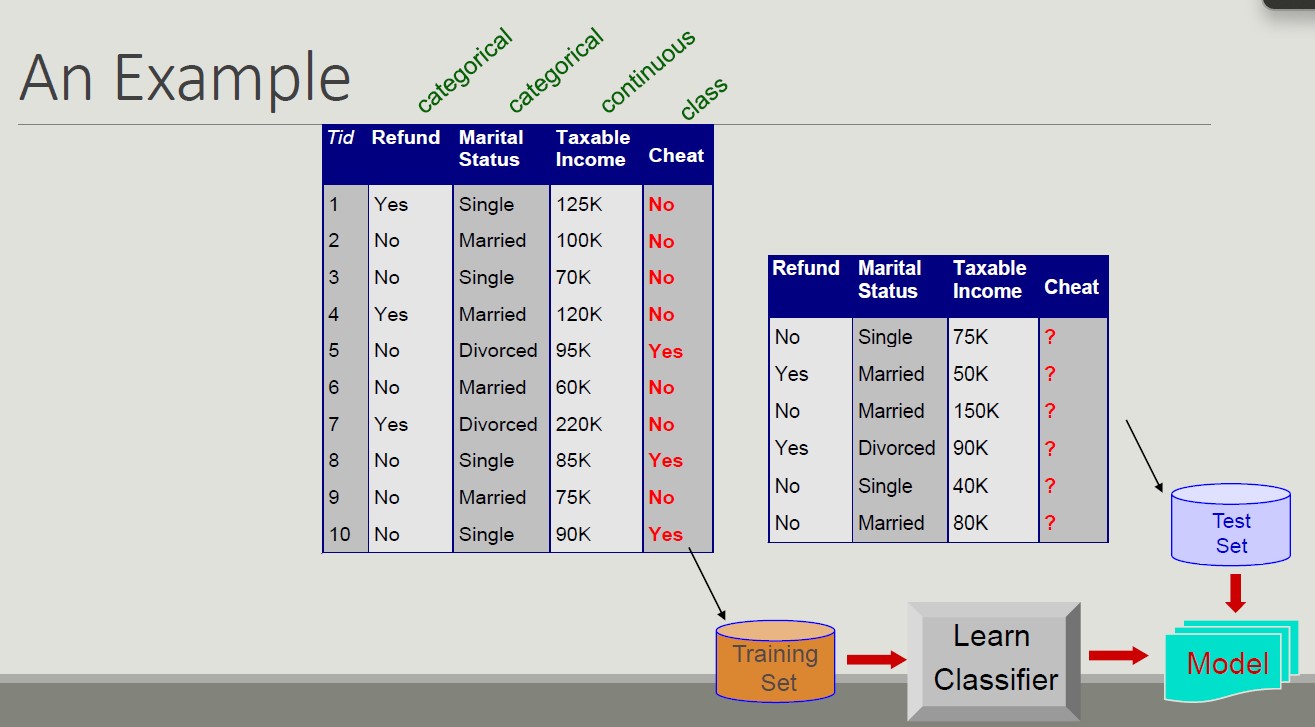
Classification example
Direct Marketing: The goal is to reduce the cost of email marketing by defining the set of customers that, with the highest probability, will buy a new product.
Technique:
- Exploit the data collected during the launch of similar products
- We know which customers bought and which one did not
- {buy, not buy} = class attribute
- Collect all the available information about each customers
- Use such information as an input to train the model
Churn Detection Predict customers who are willing to go to a competitor.
Technique:
- Use the purchasing data of individual users to find the relevant attributes
- Label users as {loyal, not loyal}
- Find a pattern that defines loyalty
Clustering example
Given a set of points, each featuring set of attributes, and having a similarity measure between points, find subset of points such that: points belonging to a cluster are more similar to each other than those belonging to other clusters
Marketing Segmentation
The goal is to split customers into distinct subsets to target specific marketing activities.
Techniques:
- Gather information about customer lifestyle and geographic location
- Find clusters of similar customers
- Measure cluster quality by verifying whether the purchasing patterns of customers belonging to the same cluster are more similar to those of distinct clusters
Association Rules example
Given a set of records each consisting of multiple elements belonging to a given collection. It produces rules of dependence that predict the occurrence of one of the elements in the presence of others.
Marketing Sales Promotion Suppose you have discovered this association rule: {Bagels,...} -> {Potato chips*}
This information can be used to understand what actions to take to increase its sales.
Data Mining Bets
- Scalability
- Multidimensionality of data set
- Complexity and heterogeneity of the data
- Data quality
- Data properties
- Privacy keeping
- Processing in real-time
CRISP methodology
A data mining project requires a structured approach in order to choose the best algorithm.
CRISP-DM methodology is the most used technique. It is one of the most structured proposals to define the fundamental steps of a data mining project.
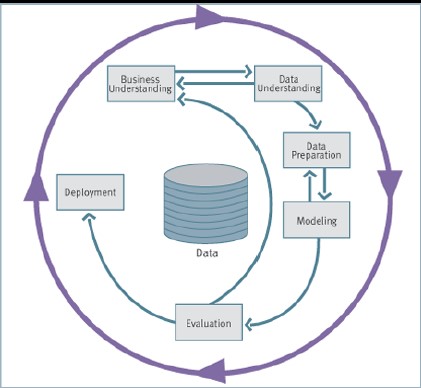
The six stages of the life cycle are not strictly sequential, indeed, it is often necessary.
- Business understanding (understand the application domain): understanding project goals from users' point of view, translate the user's problem into a data mining problem and define a project plan.
- Get an idea about the business domain and the data mining approach to adopt.
- Data understanding: preliminary data collection aimed at identifying quality problems and conducting preliminary analysis to identify the salient characteristics.
- Data preparation: tasks needed to create the final dataset, selecting attributes and records, transforming and cleaning data.
- Prepare the data for ML tasks (clean, complete missing data, create new features)
- Model creation: data mining techniques are applied to the dataset in order to identify what makes the model more accurate.
- Evaluation of model and results: the model obtained from the previous phase are analyzed to verify that they are sufficiently precise and robust to respond adequately to the user's objectives.
- Deployment: the built-in model and acquired knowledge must be made available to users.
- Change the software and processes to include new AI functionalities
Different classes of data mining use different algorithms so the evaluation changes accordingly.
Created: September 20, 2022 07:20:18