Pattern Recognition
Pattern recognition is the discipline that studies the recognition of patterns (data) even with pre-programmed algorithms (not able to learn automatically)
The model is a set of hand-crafted instructions.
Technique similar to the Expert System developed in the '80, which was a first form of artificial intelligence. The ability of a calculator to perform calculations on large amounts of data is exploited.
The programmer develops a series of instructions to solve specific problem:
- These instructions are typically based on if-then-else statements
- A strong priori knowledge of the problem is required
Problems that can be faced with explicitly programmed instructions:
- The conditions are stable and known a priori (constrained industrial environment)
- There are mathematical formulas to model the problem
- The problem must be limited in dimensionality and not too complex
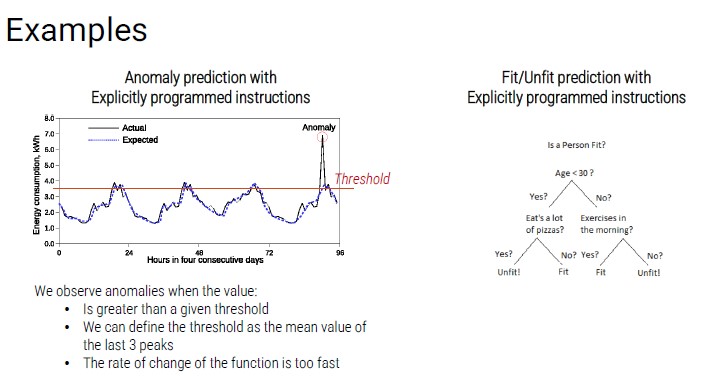
Explicitly Programmed Instructions
General and technical considerations about pattern recognition:
- It can achieve a high degree of success if the a priori knowledge is adequate, dimensionality of the problem is limited and the test domain is similar to what was assumed when defining the instructions
- The developed solution will inevitably be specific
- There is not a real learning phase
- It is possible to understand why the developed system fails in classification
- If the problem becomes complicated, the programming time increase
- The code risks becoming unmanageable due to:
- High complexity and number of innested statements
- Length of code
- Too specific functions
Limits of programmed instructions

Solving these problems with instructions is very complex. The level of generalization of the proposed solution would be very limited.
It is necessary, when needed, to address the problems with other paradigms.
Created: October 19, 2022 12:59:15